Key Takeaways
- Assess your home’s power requirements to determine the generator size.
- Understand the advantages and disadvantages of various fuel types.
- Consider professional installation for safety and efficiency.
Power outages can disrupt daily life, cause costly damage, and create uncomfortable—or even unsafe—conditions at home. Investing in a reliable generator is a smart choice for homeowners who want to ensure their property remains powered, regardless of the circumstances. The process of selecting a generator involves more than just picking a model; understanding your unique requirements, the available technologies, and safety practices is key. To get expert help or installation services, you can trust Dacula generator installation specialists to guide you through every step, from assessment to final setup.
With the growing variety of generator options, knowing the differences in types, fuel sources, installation, and upkeep can be overwhelming. This guide is designed to walk you through each step of the decision-making process, helping you confidently select the ideal generator for your household. Taking these measures ensures that you’ll be ready for anything and able to maintain comfort and security in your home.
Generators come in several shapes and sizes, from portable models designed for occasional use to powerful whole-home systems that activate automatically. Knowing your priorities can help you pick between convenience, power capacity, and budget. Not only can the right generator keep crucial systems running—such as medical devices, refrigeration, and HVAC—it can also save you from unexpected expenses due to spoiled food or frozen pipes.
Assessing Your Power Needs
Start by making a list of every appliance and essential system you want to power in an outage. Each device typically lists its wattage, either on the label or on the manufacturer’s website. Typical wattages include:
- Refrigerator: 600 watts
- Sump pump: 750 to 1,500 watts
- Portable heater: 1,500 watts
- Window air conditioner: 1,000 watts
- Lights: 5 to 80 watts per bulb
- Computer or other robotic device: 60 to 300 watts
Sum these numbers to estimate the total generators capacity you’ll need. Experts recommend using a generator rated at least 10–20% above your calculated requirements to account for momentary surges when appliances start up. If your household includes medical equipment or high-power appliances, consider consulting a professional to perform a load assessment.
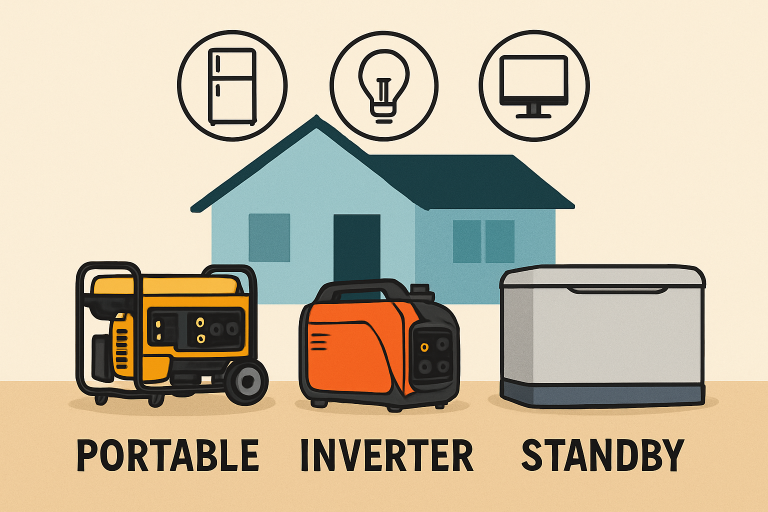
Types of Generators
The right generator type depends on your lifestyle and the risks of outages. Options include:
- Portable Generators: Affordable, suitable for short-term use, and easy to store, but generally need manual startup and fueling. They’re ideal for powering a few key appliances simultaneously.
- Inverter Generators: Operating quietly and efficiently, these generators provide a stable voltage perfect for electronics and sensitive devices. They’re lightweight and often favored for camping or small households.
- Home Standby Generators:Permanently installed outside your home, these generators turn on automatically during outages and can supply power to your entire house or essential circuits without requiring any manual intervention.
Fuel Options
Different generators run on one or more of the following fuels:
- Gasoline: Readily available at gas stations, but has a shorter shelf life and is more volatile. Requires safe storage and fuel stabilizers for long-term readiness.
- Diesel: Known for power and efficiency, diesel generators are a good fit for frequent, heavy usage. They generate more noise and require special storage consideration, but can last longer with routine care.
- Propane: Delivering cleaner burns and longer shelf lives than gas, propane needs properly sized tanks and installation by professionals. It can also be used in dual-fuel units for flexibility.
- Natural Gas: Directly connects to a home’s gas line, offering an uninterrupted supply (unless the infrastructure is compromised). It’s one of the most convenient options, but it’s less viable during earthquakes or other disasters that affect utilities.
Fuel choice often depends on local availability and logistics for storage.
Installation Considerations
Proper setup is essential for safe and reliable operation:
- Location: Install generators on flat, non-flammable surfaces at least 18 inches from the house, keeping exhaust away from doors and windows.
- Permits: Research local building codes to determine if permits or inspections are required, especially for standby systems, which need to meet residential safety standards.
- Professional Installation: Experts recommend professional installation for standby or whole-home generators, ensuring proper electrical and fuel connections.
This step not only safeguards your investment but also verifies compliance with all legal and insurance requirements.
Maintenance Requirements
Following a maintenance schedule maximizes service life and reliability:
- Change oil after the first 25 hours of use, then every 50–100 hours, or as specified by the manufacturer.
- Check, clean, or replace air and fuel filters regularly.
- Inspect spark plugs and batteries for corrosion and ensure they are charged.
- Test-run the unit monthly to ensure readiness in the event of an emergency.
Neglecting these routines could lead to equipment failure when you need power most.
Cost Analysis
The initial price of a generator is only part of the total expense to consider. On average:
- Portable Generators: $500–$2,000
- Inverter Generators: $1,000–$3,000
- Home Standby Generators:$2,000–$7,000, with professional installation adding $2,500–$4,000
It’s wise to budget for fuel, maintenance, and any necessary accessories or permits when evaluating the total cost.
Safety Tips
Generator misuse can be hazardous. Always:
- Operate the unit outdoors in well-ventilated spaces to avoid carbon monoxide buildup.
- Use extension cords rated for outdoor use and the generator’s wattage output.
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home before using a generator.
- Keep the generator dry and protect it from precipitation or standing water.
Prioritizing these precautions helps prevent accidents and ensures dependable backup power.
Final Thoughts
Home generators offer invaluable peace of mind and protection against the unpredictable. Carefully assess your household’s power needs, choose the right type and fuel, and prioritize professional installation and ongoing maintenance to ensure optimal performance. By making an informed decision, you ensure your family’s safety and comfort during power failures—and maintain the stability of your daily life no matter the weather or emergency.





No Comments